09 / 07 / 2016
Everyone is exposed to a variety of infectious agents in the environment such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Any seasonal change challenges our immune system with new pathogens. This year - even before the start of the flu season - the World Health Organization has declared Zika virus infections an international public health emergency. The Zika virus is not a new virus and is similar to other viruses transmitted by mosquitoes such as West Nile virus, dengue, yellow fever, and Japanese encephalitis. The symptoms of Zika virus infection are similar to normal flu symptoms. They include fever, headache, muscle and joint pain, rash and conjunctivitis. Often there are no symptoms, and in most cases people are not aware that they are infected while they are spreading the virus. Currently, mosquito control is the only way for prevention from Zika infection and there are no treatments available. Therefore, it would be prudent to understand how to support our body’s immune system and protect it against Zika or other viral and infectious pathogens.
08 / 19 / 2016
Vitamin C is a vital nutrient for human health and survival. It is not only a powerful antioxidant and immune booster, but it also supports collagen connective tissue formation and builds extracellular matrix, which is the “glue” that binds the body’s cells together. It is important for faster wound healing and prevention of various chronic conditions. Optimum amounts of vitamin C effectively protect the body and cardiovascular system against biological rusting. Additionally, there are several other important functions of vitamin C. It is a cofactor for a series of biological enzymes, which are important for the improved metabolism of cholesterol, triglycerides and other risk factors of heart disease. It is an important energy molecule needed to recharge energy carriers inside the cells. Vitamin C is essential for production of carnitine, the molecule that carries fatty acids into the mitochondria for energy production. It participates in biological recycling of vitamin E, glutathione and many other cell protective molecules, and when taken together with calcium, it increases calcium absorption. Vitamin C neutralizes various toxins in the body, and protects healthy cells from harmful substances and the effects of many pharmaceutical drugs.
08 / 04 / 2016
In the last Health Science News Page, we elaborated on the important role of lipoprotein (a), or Lp (a), acting as a surrogate for vitamin C. Lp (a) is a sticky molecule that contains a large protein chain called apolipoprotein(a) or apo(a) attached to a molecule of low-density lipoprotein (LDL). As such, the Lp (a) helps in transporting cholesterol and triglycerides in the body. In addition, the presence of apo(a) gives this molecule other distinct features such as its ability to “stick” to collagen and other structural proteins and to facilitate blood clotting. Lp (a) is found only in humans and animals that do not produce their own vitamin C, and its appearance in human metabolism coincides with a loss of vitamin C production in the ancestors of man. Today, the only reasonable explanation for these events remains Dr. Rath’s discovery that Lp (a) is a functional substitute for vitamin C as a temporary “repair factor” for damaged blood vessels caused by chronic deficiency of vitamin C.
07 / 22 / 2016
Cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide. The World Health Organization’s International Agency for Cancer Research has projected that as the life expectancy increases, cancer diagnosis will increase by 75%-90% by the year 2030. While enormous amounts of money are being spent on cancer research, there is still no cure in sight. This is because the cancer research establishment largely cultivates already tried conventional approaches and has become reluctant to trying and embracing new concepts and innovative thinking.
07 / 11 / 2016
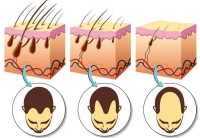
Although in our society it has gained cosmetic importance, hair on the head and entire body is one of the distinguishing characteristics of mammals. The main function of hair is to regulate body temperature by facilitating evaporation of sweat in hot weather and to create additional insulation by closing the skin pores in cold weather. Despite its important function, the hair shaft itself is not living tissue. Tiny blood vessels at the base of every hair follicle feed the hair root to keep it growing. Yet, the hair we see on the body contains only dead cells. As the new cells grow at the base of the hair follicle, the older cells die and are forced along the follicle towards the scalp. It is normal to shed approximately 100 to 150 hairs a day. Hair is made of a protein called keratin, and hair color is determined by the presence of melanin secreted by pigment cells. As we age, these pigment cells die and the hair turns gray.
06 / 25 / 2016
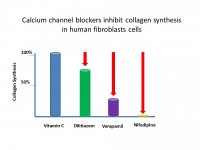
The drugs intended to reduce blood pressure, correct arrhythmias and some forms of heart disease are the most commonly prescribed drugs in the US. One in every three adults, or approximately 75 million people, is diagnosed with high blood pressure in the US and many more have pre-hypertension. About 15 million people have some form of irregular heartbeats or arrhythmias. The most commonly prescribed drugs to treat these and other conditions are the so called “channel-blockers” or “agonists” which include calcium, sodium and potassium channel blockers. Worldwide sales of these drugs have reached $6 billion. In the United States, calcium channel blockers are the eighth largest drug class in prescription sales.
06 / 13 / 2016
The global supplement market is $82 billion, and the US supplement industry contributes $37 billion to that number. Consumers spend billions on dietary supplements trusting in their beneficial effects. Faced with countless options and a worldwide market, choosing supplements can be overwhelming. Rarely are consumers supplied with sufficient scientific information to base their decisions on and usually they only have a company’s marketing materials. Dr. Rath Research Institute conducts academic research in the area of natural health and provides a scientific basis for the development of unique synergy based micronutrient combinations.
05 / 24 / 2016
A synergistic combination of micronutrients comprised of various vitamins and minerals is essential for survival and maintaining optimal health. Vitamins are organic substances produced by plants or animals, while minerals are inorganic elements present in the soil and water and are absorbed by plants. The main source of minerals for humans is through the plants we eat. However, a study published in 2004 in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition concluded that in the past fifty years there has been significant decline in the nutritional content of vegetables and fruits with regards to the amount of vitamins C and B2, protein, calcium, iron, and phosphorus. Based on their results, the authors estimated that there would likely have been similar declines in other nutrients as well, such as magnesium, zinc, and vitamins B6 and E. Aggressive farming practices, and the abundant use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and other harmful chemicals are the main reason for the nutritional decline. It is claimed that today one would have to eat eight oranges to derive the same amount of Vitamin A as our grandparents would have obtained from one.
05 / 14 / 2016
Muscles are contractile connective tissue that help in the movement of various organs in the body. Approximately 50% of human body weight consists of the muscle weight. There are three types of muscles in the body: skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles, with each one having very specialized structure and functions.
05 / 02 / 2016
Connective tissue is the most abundant type of tissue in our body. The shape and form of the body, including its organs, muscles, bones, and cartilage, are determined by the properties of connective tissue. Skin, blood, blood vessels, adipose tissue (fat cells), tendons, ligaments, and teeth are various examples of connective tissue. Therefore, the term “connective tissue diseases” encompasses a wide range of ailments; some of them are inherited, while others develop as autoimmune diseases due to excessive inflammation. Examples of autoimmune connective tissue diseases are scleroderma, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), mixed connective tissue diseases, etc.
04 / 17 / 2016
According to a recent study published in The Lancet medical journal, the number of people diagnosed with diabetes has increased four times in the past 35 years1. There were 108 million people diagnosed with diabetes in 1980 and 422 million in 2014. Based on this alarming statistical finding, the World Health Organization (WHO) selected diabetes as the theme for World Health Day 2016 in order to raise awareness and to prevent and effectively manage diabetes.
04 / 04 / 2016
Athletes focus on increasing stamina, reducing muscle fatigue and injuries, and maximizing performance. While they recognize the role of macronutrients such as proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and other healthy foods, the importance of micronutrients is often neglected. Insufficiency of micronutrients frequently leads to easy fatigue, muscle or bone injury, and other ailments like arthritis. An intense exercise routine and increased metabolic turnover makes micronutrient supplementation essential for athletes.
03 / 21 / 2016
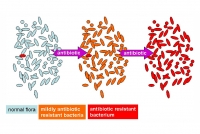
Globally, resistance to treatment with antimicrobial drugs is becoming an increasingly serious public health problem. Antimicrobial resistance is a larger phenomenon than antibiotic resistance. In addition to drug resistant bacteria, the antimicrobial resistant species also include other drug resistant microbes such as fungi, parasites, and viruses. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 480,000 new cases of multi drug resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) were diagnosed in 2013. Other disease causing and highly virulent organisms that have already developed drug resistance are malarial parasites, the fungus Candida, methicillin-resistant-Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and the bacteria causing gonorrhea. The drug resistant bacteria are estimated to cause 99,000 deaths in U.S. hospitals every year.
03 / 06 / 2016
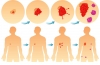
After heart disease, cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide. One in two men and one in three women will be diagnosed with some type of cancer in their lifetime. Despite novel initiatives, the American Cancer Society estimates that by 2020 the number of new cancers will increase to more than one million cases per year in men, and more than 900,000 cases per year in women. Melanoma, lung, breast, and prostate cancer are the most commonly diagnosed among the new cancers. Although cigarette smoking - the most common risk factor for cancer - still remains high, obesity and other metabolic disorders can contribute to and increase breast, colon, uterus, pancreas, and kidney cancers.
02 / 19 / 2016
Cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes, continue to be the leading causes of deaths resulting in more than 17 million deaths each year worldwide. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) manifests as atherosclerosis, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, arrhythmia, and heart failure and has many more symptoms affecting the heart and blood vessels. Additionally, other metabolic diseases such as obesity and diabetes further increase the risk of CVD.
02 / 08 / 2016
Lyme disease (LD), also called Borreliosis or Lyme borreliosis, is a bacterial infection transmitted by ticks. Statistics confirm that LD has become the most common vector-borne illness in the USA and Europe, although its occurrence has been documented on all continents except Antarctica. LD is caused by the bacterium of genus Borrelia that is harbored in ticks. Borrelia can be found frequently in small and large mammals, and birds and reptiles on which many ticks feed and mate making them prone to become infected. The ticks that spread LD can sometimes co-transmit other tick-borne pathogens such as Ehrlichia sp., Babesia sp., and Bartonella sp.