More than two years after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic that claimed up to 6.5 million deaths, the world is still struggling to find an effective solution to preventing this infection. Despite global spending of roughly $100 billion (a figure that could rise to $160 billion by 2025) on the COVID-19 vaccines, currently used vaccines are not effective against preventing infections and viral spread and can only lessen severe symptoms of COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 has been undergoing numerous mutations and currently about 90% of COVID-19 cases involve the Omicron variant. Although these variant infections are less severe than caused by the original strain, Omicron spreads faster and is dangerous for the immunocompromised and high-risk individuals.
Marine plants, either marine algae or seaweeds, were part of the daily diet of our ancestors and have been consumed in different parts of Asia for centuries. Although plants like kelp, nori, dulce, and spirulina are more commonly used in sushi, Asian soups, snacks, or seasonings, there are many other varieties of sea plants packed with important nutrients. These sea vegetables absorb beneficial nutrients from the ocean and are very good sources of protein, fiber, healthy polyunsaturated fats, antioxidants, and vitamins and minerals. For example, after iodized salt they are the second richest source of iodine, and it is well known that iodine is critical for a healthy thyroid gland. Thyroid hormones - thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3) - play a vital role in growth and development of the body and in regulating various metabolic processes, including basic metabolic rate, healthy functioning of the brain, heart, immune and digestive systems, and building strong muscles and bones. Two sea plants which contain critical nutrients for overall health are Irish moss and bladderwrack.
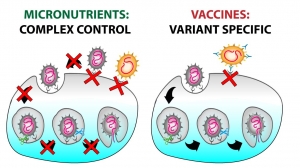
In addition to the continuing COVID-19 pandemic and the omicron wave, the flu season is also upon us. As we have already learned, the RNA/DNA vaccines have severe limitations in preventing coronavirus infections, emerging viral mutants and their spread, and seasonal anti-flu vaccines cannot keep up with the viral mutations. It is difficult to protect ourselves from every single infectious agent unless our own immunity is strong. Most of the antivirals weaken the immune system and cause other side effects. It is critical to address the fundamental mechanisms of infection and increase the immunity of the human population.
Diabetes is the one of the fastest growing non-communicable diseases worldwide. It is associated with high blood sugar levels, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and kidney problems. It increases one’s risk of serious COVID-19 outcomes, as 40% of people who have died of COVID-19 also had diabetes. Currently, 1 in 11 adults in the world has diabetes, and it is estimated that by 2050 almost 1 in 3 people will have diabetes or pre-diabetes. More than 34 million Americans have diabetes and 7.5 million have pre-diabetes. With such staggering statistics, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has declared November as Diabetes Awareness Month to prevent and effectively manage this disease.
Despite availability of vaccines, more than 2000 people die every day in the US alone due to COVID-19 and approximately 133,000 new cases are reported daily.1 Currently, more than 182 million Americans, or 54%, are considered fully vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, and approximately 64% of the population has received at least one vaccine dose. However, reports indicate that vaccine efficacy reduces with time and booster doses are now recommended despite a lack of unity from the FDA and CDC experts in accepting this step. Moreover, new variants of the coronavirus further complicate the picture, and “breakthrough infections” in the fully vaccinated are on the rise. This situation calls for the revision of current approaches and incorporation of innovative health strategies that are effective, economic, and accepted by the majority of people worldwide.
More than a year after the emergence of COVID-19 the world is still at a standstill facing rapid spread and new mutations of SARS-CoV-2. Many countries are struggling to have any grip on this pandemic and dealing with scarcity of new vaccines. Despite implementing preventive measures like hand washing, masks, and social distancing, the daily infections and deaths attributed to COVID-19 continue to rise.
Worldwide, 2.2 million people died of this infection with upwards of 104 million COVID-19 cases. Drastic lockdowns threw millions of people into extreme poverty, hunger, and malnutrition, and due to lack of access to nutritious food, more people have compromised immunity, thus increased susceptibility to infections. Although pharmaceutical companies are racing to produce drugs and anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccines became available, their efficacy is now being questioned with rapidly mutating coronavirus variants. It is a well-known fact that people with pre-existing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer have impaired immunity and are prone to serious complications from COVID-19. In this critical situation, several clinical trials have been conducted with vitamin C and other nutrients in COVID-19 patients, some with promising results. Health care providers also turned to natural approaches to improve immunity and curb the spread of infections.
Vitamin C is a vital nutrient for human health and survival. It is well known that the human body does not produce vitamin C, and it must be obtained from food sources and dietary supplements. Yet, a clinically significant deficiency of vitamin C is the fourth leading nutrient deficiency in the US.
Recently, vitamin C has gained a renewed importance in the COVID-19 pandemic because of its immune modulating properties. Although not approved as a treatment of COVID-19, intravenous vitamin C was one of the first options successfully used in several hospitals in New York, China, Italy and other places at the peak of COVID-19. A review of 18 clinical trials covering more than 2000 patients analyzed the effect of vitamin C and ICU stay. The authors stated that in at least six of those clinical trials even oral vitamin C doses of 1-3 g/day were enough to reduce the ICU stay by 8.6%.*
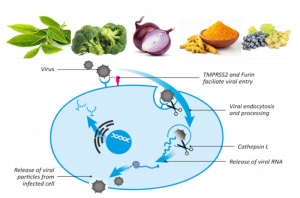
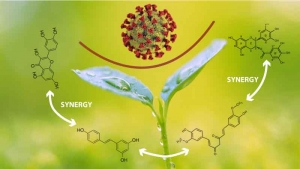
Plants are the rich source of many nutrients that protect them from diseases, heat, radiation, poisons, and pollutants. These phytonutrients also have numerous health benefits for humans as they provide antioxidant protection to our body’s cells, fight inflammation, and can boost immune system function. In the developed countries, active plant components have been known to be effective against leading health problems, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Recently, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the phytonutrients such as green tea extract, quercetin (present in red onions), resveratrol (present in red grapes), and curcumin (turmeric root extract) have gained renewed interest in their antiviral benefits. However, despite promoting the consumption of 8-10 daily servings of fruits and vegetables, less than 4% of Americans meet these recommendations. Did you have your veggies today?
Here we outline the health benefits of key phytobiological components:
Quercetin is proven to benefit against RNA viruses (coronavirus, flu) and DNA viruses (herpes). It helps in thwarting viral multiplication by killing the live viruses within the cells. It can also protect infected cells from damage caused by the pathogen and aid in the cell repair process.
Curcumin from turmeric root extract is a very potent antiviral and anti-inflammatory agent. It inactivates viruses at multiple steps of infection. First, it can inhibit viral attachment to the cell thus blocking the viral entry. It also prevents viruses from becoming active by blocking production of viral proteins and inhibits the multiplication of viruses and their release from the cells. This stops the spread of infection. Curcumin also protects against widespread inflammation caused by a viral infection. We learned that the so-called “cytokine storm” caused by extensive inflammation is one of the main causes of serious complications in COVID-19. Curcumin has shown benefits against influenza and other types of viruses including dengue, herpes, hepatitis (HBV), papillomavirus (HPV), and leukemia (HTLV). Unlike to antiviral drugs, the viruses have not shown resistance to curcumin.
Green tea extract is known to reduce influenza infections in healthcare workers despite their exposure. In November 2020 there are expected results coming from a large clinical trial testing whether green tea extract also protects the healthcare workers against COVID-19. At the cellular level, green tea extract demonstrated benefits against the coronavirus by inhibiting a key enzyme involved in its multiplication. Similar to curcumin, green tea extract showed antiviral action against influenza A and B viruses, HIV, hepatitis C and Zika viruses. Green tea extract can weaken the coronavirus by inhibiting its outer proteins and can also prevent its attachment to the cells.
Resveratrol and cruciferous vegetable extracts. Resveratrol from grape seeds has been known for its heart-protective effects. However, resveratrol also has antiviral properties and is effective in reducing viral multiplication and inflammation caused by viral infection. The antiviral efficacy of resveratrol includes against viruses such as influenza A and B, SARS-CoV, and rhinovirus (which causes the common cold). Resveratrol and the cruciferous vegetable extracts support the body’s immune system thus contributing to their protective benefits.
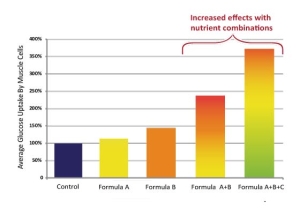
Cooperation of nutrients for enhanced benefits. Our body does not rely on one micronutrient to protect itself against microbial invaders. In addition to active plant components, it requires many vitamins and minerals to mount effective protection. Research conducted at the Dr. Rath Research Institute has documented how various nutrient combinations can enhance healthy cellular functions. In our recent studies we tested how micronutrients can impair the coronavirus in entering the cells in our body 1, 2. We showed, among others, that a specific combination of phytonutrients can inhibit binding of a viral protein to the cell receptors by 97% and can also inhibit the expression of these receptors on the cells by 92%, thereby reducing the potential sites for virus attachments.
Considering the impact of the current pandemic on public health and the economy and a lack of effective treatment options, safe natural compounds with scientifically proven efficacy should become part of a public health strategy and implemented without delay.
Ref:
1. Ivanov V, et al., J CM & NH, July 200
2. Goc A, et al., J CM & NH, Aug 2020
During the current COVID-19 pandemic, we have learned that having diabetes significantly increases one’s chances of developing serious complications which could potentially be life-threatening. Although diabetes has increased globally, it has exponentially risen in the developing countries due to sedentary lifestyles, and fast food diets rich in artificial sugars and fat which can lead to obesity and other disorders. Obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and impaired glucose metabolism are now collectively called metabolic syndrome.
During the current coronavirus pandemic, diabetes has become a serious concern. People with type 1, type 2 and pregnancy-related (gestational) diabetes are at a higher risk of developing serious complications from COVID-19 which could potentially be life-threatening. Having diabetes reduces a person’s immunity and thereby increases the chances of contracting any viral or bacterial infection and having delayed recovery.