Benefits Of Micronutrient Synergy In Bladder Cancer
Cancer of the urinary bladder is the fourth most common cause of cancer in men. Most bladder cancer patients tend to be older men over the age of 60. The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2015, approximately 74,000 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the US.
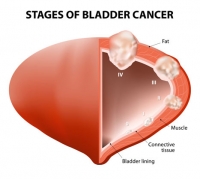
The human urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureter (the tubes carrying urine from the kidneys to the bladder), urinary bladder and the urethra. The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular sac located in the pelvis, and its main function is to store urine before it is excreted. The urinary bladder can store about 400-600 ml of urine. It is lined by a specific type of cells called urothelium, which separate the urine from the muscular layer of the urinary bladder. Ninety percent of cancers of the urinary bladder, called urothelial carcinomas, develop in this cell layer. While the overall five-year survival rate of localized bladder cancer limited to the urothelium is quite good, the survival rate reduces drastically when the cancer spreads to the muscular layer of the bladder, and to the lymph nodes and beyond. In 2015 in the US, 16,000 deaths are projected to be due to metastasized urinary bladder cancer.
Along with age, gender, and tobacco use, chronic urinary tract infections can also increase the risk of urinary bladder cancer. In addition, occupational and chemical exposure to arsenic, benzene in the paint industries and aromatic amines from the leather, rubber, and textile industries increase the risk of urinary bladder cancers. Chemotherapy drugs (cyclophosphamide) and diabetes drugs (Actos) have also been blamed for increased incidences of urinary bladder cancers.
The symptoms of the cancer of the bladder are vague and in older men especially they may often be missed, as they could relate to other non-cancerous conditions as well. Fresh blood or clots in the urine may indicate cancer. However, other symptoms such as low back pain, frequent urination, difficulty in urination, could also be the signs of urinary infection, kidney stones or enlarged prostate, and therefore, could delay the diagnosis of cancer. In many cases, bladder cancer is diagnosed when the disease is already spread and thus the survival rate reduces to 6% when the bladder cancer is diagnosed at an advanced stage.
More than 90% of the cancer deaths occur due to the spread of cancer. The connective tissue digesting enzymes - matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) - play a significant role in cancer metastasis. We used a specific combination of micronutrients containing vitamin C, lysine, proline, green tea extract, and others to evaluate the activity of MMPs in urinary bladder cancer cells. The micronutrients were able to inhibit specific types of MMP enzymes (MMP-2 and MMP-9) up to 100%. Additionally, we also noted that the micronutrient combination induced apoptosis (natural cancer cell death) in the bladder cancer cells1.
The current treatment options for bladder cancer are surgical removal of the urinary bladder, and depending on the extent of metastasis, chemotherapy, and radiation, along with associated side effects. Our research results in the area of natural health could be encouraging information for the patients and physicians to discuss how to stop the spread of urinary bladder cancer cells.
1. Ref: MW Roomi et al., Anti-Tumor Effect of Ascorbic Acid, Lysine, Proline, Arginine, and Green Tea Extract on Bladder Cancer Cell Line T-24; International Journal of Urology 2006, 13(4): 415-419.