Research Supports Efficacy of Natural Approaches in Breast Cancer
October is designated as Breast Cancer Awareness month. With the exception of skin cancer, breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in the US, and about 1 in 8 women are likely to develop it during their lifetime. According to 2022 estimates, approximately 339,250 new cases of breast cancer will be diagnosed in women, and 2710 new breast cancers will be diagnosed in men in the USA. Although, breast cancer is rare in males it still contributes to 1% of all breast cancers and this number is rapidly increasing. Due to lack of awareness regarding male breast cancer, it is often diagnosed at a later stage and is therefore difficult to treat.
In general, any cancer involves multiple stages of progression; however, the basic feature of cancer is excessive and continuous multiplication of abnormal (cancerous) cells leading to tumor formation. The aggressiveness of a cancer is determined by its ability to spread (metastasize) to other organs. The collagen matrix surrounding the cancer cells plays a crucial role in the spread of cancer and its integrity is critical to keeping cancer cellular growth in check. An ample amount of vitamin C, the amino acids lysine and proline, and other nutrients are essential for the strength and stability of the collagen tissue.
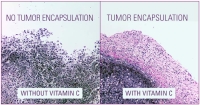
Since chemical exposure is one of the important factors in the development of breast cancer, the scientists at the Dr. Rath Research Institute evaluated a combination of micronutrients containing vitamin C, lysine, proline, green tea extract, and others, on the development of chemically-induced mammary tumors in rats1. We observed that the supplementation of micronutrients effectively reduced the number of tumors by 68%. In another study, we also evaluated the effects of vitamin C supplementation on the development of breast cancer in a unique strain of mice that lost their ability to produce vitamin C2. We found that the mice supplemented with vitamin C developed 28% smaller tumors, and had fewer areas of necrosis. More importantly, the tumors were surrounded by a dense collagen capsule thereby minimizing their potential of metastasis.
Additionally, a deficiency of vitamin D has also been associated with several chronic diseases including breast cancer. In a recent study3, we tested the effects of vitamin D alone, and in combination with a group of synergistic micronutrients on breast cancer. The results showed that vitamin D in combination with the synergistic micronutrient mixture had a significant effect on reducing the growth of breast cancer cells. With increasing doses of the micronutrient mixture, breast cancer cell growth was inhibited by as much as 94%.
In search of effective natural means to impair the growth of estrogen-dependent breast cancer cells, our scientists evaluated the effects of micronutrients and natural estrogenic compounds from soy and other plants. We investigated the effect of estrogen and several natural compounds individually and as a combination on the growth of breast cancer cells. Our results showed that the combination of these compounds inhibited the growth of cancer cells by 40% more than in the control.
Despite a variety of expensive treatment options, the long-term outlook for breast cancer remains poor. While breast cancer awareness in October emphasizes early cancer detection and treatment, it is critical to bring up the importance of cancer prevention and control with natural non-toxic approaches. Our studies prove that a combination of specifically chosen micronutrients works together significantly better than any individual compound on multiple stages of cancer progression.
Ref:
1. M.W. Roomi, et al., Breast Cancer Research 2005, 7:R291-R295.
2. J. Cha, et al., International Journal of Oncology 2013, 42: 55-64
3. V Ivanov et al., J CM & NH, June 2019