Elijah Artman
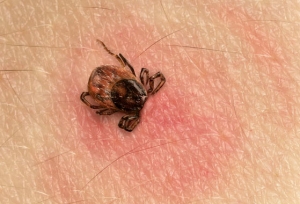
Lyme disease (LD), also called Borreliosis or Lyme borreliosis, is a bacterial infection transmitted by ticks. Statistics confirm that LD has become the most common vector-borne illness in the USA and Europe, although its occurrence has been documented on all continents except Antarctica.
LD is caused by the bacterium of genus Borrelia that is harbored in ticks. Borrelia can be found frequently in small and large mammals, and birds and reptiles on which many ticks feed and mate making them prone to become infected. The ticks that spread LD can sometimes co-transmit other tick-borne pathogens such as Ehrlichia sp., Babesia sp., and Bartonella sp.
Lyme disease (LD) is the most common vector-borne disease in the USA (approximately 30,000 cases annually) and in Europe (approximately 65,000-80,000 cases annually). However, current statistics reflect only reported cases, and the actual numbers may be even 5-10 times higher due to frequent misdiagnosis of the disease.
Lyme disease manifests itself as an inflammatory disease that can affect many organs in the body. In its early stage (localized) it affects mainly the skin. In later stages (disseminated and chronic) the inflammation spreads to the joints, nervous system and, to a lesser extent, the heart, muscles or other organs.