Elijah Artman
The uterus, commonly referred to as the “womb,” is a hollow and highly expandable organ responsible for accommodating the growing fetus during the nine months of pregnancy. The uterus is made up of strong, involuntary muscles that contract during menstruation and childbirth. Abnormal contractions of the uterine muscles may cause severe cramps during menstruation. During pregnancy, the abnormal and untimely uterine contractions could lead to premature labor and delivery. A normal healthy pregnancy usually lasts up to 40 weeks. If the infant is born before the 37th week of pregnancy, it is termed a “preterm birth.” According to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 11.4% of the pregnancies in the US ended in preterm delivery in 2013. Preterm delivery is also the cause of approximately 35% of all infant deaths.
The nutritional requirements of men and women differ. A woman’s body needs extra nutritional support during various physiological transitions such as puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, lactation, and menopause. Women are affected by different health problems than men and are more often diagnosed with autoimmune diseases, arthritis, osteoporosis, and depression. Despite popular belief that heart disease is a male problem, one in four menopausal women die from heart disease making heart disease, not cancer, the major cause of death of American women. At different stages of life, women benefit from properly selected micronutrients to assure the optimum function of the cells building the nervous, immune, cardiovascular, and endocrine systems.
Over 3 million Americans over 40 suffer from some sort of visual impairment. Vision loss is one of the major causes of disabilities, and age related eye diseases (AREDs) are rapidly becoming a public health problem in developed countries. Visual impairment caused by AREDs can lead to other serious health issues, including decreased mobility, depression, hip fractures, other accidents, and an overall lower quality of life. Most AREDs do not have effective treatments and it is important to maintain eye health and to prevent vision deterioration.
Scurvy (known as “Sailor’s disease”) is a condition resulting from a complete depletion of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). It is a fatal disease characterized by a slow dissolution of connective tissue throughout the body including the walls of the blood vessels. This disease was quite common in earlier centuries, especially among sailors whose diet was deprived of vitamin C. During long voyages at sea many died within months from tremendous blood loss. Today fully developed scurvy is rare; however, subclinical scurvy is very common especially in the elderly, infants, children on special diets, and people with poor dietary habits.
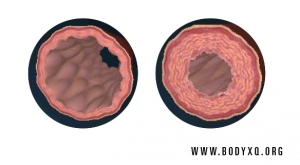
Heart attacks and strokes have consistently remained the leading causes of deaths. Atherosclerosis, the underlying cause of these diseases, results in 17 million deaths each year. Yet, high blood cholesterol levels, a fatty diet, and obesity have been blamed as the causes of heart disease. However, cutting down dietary fat and the artificial reduction of blood cholesterol with cholesterol-reducing medicines have not been successful in addressing this issue. Atherosclerotic plaques occur primarily in the coronary arteries rather than in the entire 60000-mile-long vascular system. The absence of plaque in the veins and the fact that animals do not suffer from atherosclerosis while humans do cannot be explained by conventional medicine and the cholesterol theory of heart disease.
Heart Failure is a serious health condition where the heart is unable to pump enough oxygenated blood to other parts of the body. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 5.1 million people in the US are affected by heart failure and about 40-50% of them die within one year of diagnosis. The economic impact of heart failure is huge, as the national heart failure treatment costs average about $32 billion including the work absences. Worldwide, approximately 23 million people suffer from heart failure.
The widely available extract from green tea is a combination of different phytonutrients (polyphenols) present in the tea leaves, which claim various health benefits. Green tea polyphenols have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties contributing to their anti-cancer and cardiovascular benefits and support of overall health. Recent research also shows that green tea offers health benefits in several conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and so on.
According to recent dietary guidelines, healthy people should consume at least 5-9 (and sometimes up to 13) servings of fruits and vegetables daily (one serving equals 1 cup). Especially recommended are colorful fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins and various phytonutrients.
Polyphenols are the compounds present in various fruits, vegetables, coffee, tea, and nuts. They are being found to have certain health benefits. Resveratrol is a polyphenol present in very high concentrations in grapes, red wine, and purple grape juice, and in smaller proportion in peanuts, blueberries, bilberries, cranberries and dark chocolate. It is believed that plants produce resveratrol for protection from bacterial and fungal infection. Resveratrol is commonly known for its anti-aging actions. Most of the anti-aging properties of resveratrol could be attributed to its potent anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory actions. Additionally, resveratrol is also proven to have anti-cancer, anti-diabetic and anti-hypertensive actions. One of the proposed mechanisms of action of resveratrol may be that it affects the energy production pathways within the cells by preventing degradation of specific molecules called Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate (cAMP).
Curcumin is the most abundant natural phenol (curcuminoid) present in the Indian curry spice, turmeric, and it gives turmeric its yellow color. Turmeric powder is obtained from the rhizomes of the Curcuma longa plant. Turmeric powder is used extensively in South-Asian cooking and food preservation. Due to its various medicinal properties, turmeric is still used in Ayurvedic medicine for skin, respiratory, and gastrointestinal ailments, liver disorders, muscle sprains, joint pains, and wound healing. In the past few decades, curcumin has been studied to evaluate its anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune modulation properties.