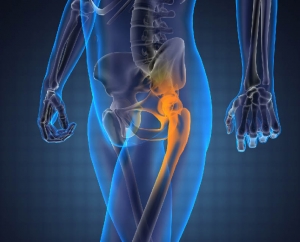
Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone cancer frequently occurring in children and young adults between the ages of 10 and 30. People over 60 are also at an increased risk. In the US, almost 800 new cases of osteosarcoma are diagnosed every year and more than 400 are in children and teens younger than 20. Initial symptoms of osteosarcoma, such as pain, bone or joint swelling, and decreased joint motion can be misleading and frequently occur in children due to sports and other injuries. In older adults, the symptoms can be misdiagnosed as arthritis.
Leukemia is a cancer of the bone marrow, which produces blood cells. Patients with leukemia experience an excessive production of white blood cells (WBCs) or leukocytes. It is the tenth most commonly diagnosed cancer in the US and is the most common cancer in children. In the US, approximately 52,380 people are expected to be diagnosed with leukemia in 2014. The numbers are equally staggering in Europe with 82,329 cases; and Asia reported 167,448 cases of leukemia in 2012. Leukemias are largely divided into acute (rapidly progressing), chronic (slower progression), myeloid, and lymphoid types depending on the type of affected cells (AML, ALL, CML, CLL). The most common type of leukemia in children is ALL, and in adults, it is AML, CML, and CLL.
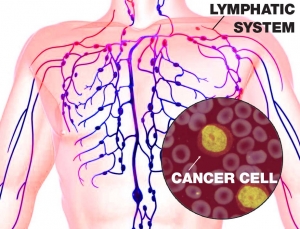
Every three minutes in the United States one person is diagnosed with some type of blood cancer. This includes cancers of the white blood cells (leukemia), various parts of the lymphatic system (lymphoma) and in bone marrow (myeloma). Lymphomas are cancers of the immune system affecting lymphocytes (a specific type of white blood cells) causing enlargement of lymph nodes. These enlarged lymph nodes are generally painless, unlike painful nodes in an infection. Such painless enlargements of the lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, and groin areas are usually one of the initial symptoms of lymphomas, and are associated with weight loss, night fevers, and other symptoms.
Tinnitus ("Tin-EYE-tus") is a symptom characterized by an auditory perception of noise - or ringing - in the ears. However, patients also describe the noise as hissing, pulsing, whooshing, clicking, or similar sounds in the ear. It is estimated that worldwide over 100 million adults are affected by tinnitus. It can disturb their daily lives with hearing loss, long-term sleep disturbances, changes in cognitive ability, challenges in employability and relationships, and it can cause depression. Although anyone can get tinnitus, tinnitus induced hearing loss is the number one service related disability for veterans costing the US government over $2.26 billion in compensation.
During the transitional period of menopause, women experience symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, irritability, mood changes and sleep disturbances. This process can take between two and three years or as long as 15 years for some women, and with widely varying severity. About 20-25% of women have severe symptoms requiring treatment. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), or menopausal hormone therapy (MHT), is a short-term treatment used to relieve menopausal symptoms experienced by women when the body stops producing the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. However, in 2002, a major clinical study called the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) was stopped because the researchers found that the risks of HRT vastly outweighed its perceived benefits. Over 80% of the women were immediately taken off of HRT because the treatment significantly increased the incidence of heart attacks, blood clots, and strokes. Later, it was also found that HRT increased the risk of certain types of cancers such as uterine, breast, and ovarian cancer, as well as liver and gall bladder diseases, thus requiring further treatment.
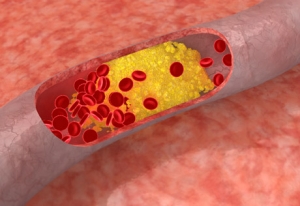
The number of people diagnosed with high cholesterol blood levels has been increasing steadily with each newly issued cholesterol guideline. Currently, about 71 million American adults and about 35% of children as young as 9 have borderline or high cholesterol levels and, as such, require cholesterol lowering medications. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 50% of adults in high-income countries and approximately 25%-35% in lower income countries have elevated cholesterol levels.
We still hold memories of the public alerts and the scare of the bird flu epidemic from 2003. Millions of infected birds were killed at that time in an effort to stop the spread of the virus to humans. Nevertheless, the bird flu virus continues to infect humans and multiple deaths have been reported since 2003. The FDA recommended antiviral flu medicines such as Tamiflu and Relenza are not very effective, and the bird flu virus has developed resistance to other flu drugs like amantadine and rimantadine.
Nearly one third of the world population is infected with the tuberculosis (TB) bacteria even if they may not have any symptoms. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 8.6 million people had active illness and 1.3 million died from TB in 20121. The US has approximately 10,000 reported cases of TB. In the developing countries, more than 90% of the TB infections and deaths occur in young adults between the ages of 15-44. The death rate is expected to increase worldwide because the TB bacteria have developed resistance to almost all the available treatment options and new approaches to TB are desperately needed.
You may be surprised to learn that the fastest growing disease in the world today is diabetes. Every day approximately 5200 Americans are diagnosed with diabetes1, which results in hundreds of cases of leg amputations, blindness, and kidney failures. Worldwide, diabetes is one of the most common non-communicable diseases and is at the forefront of the public health challenges the world faces this century. In the last two decades, the number of people suffering from diabetes has skyrocketed and it is projected to increase from 171 million in 2000 to 438 million in 2030.
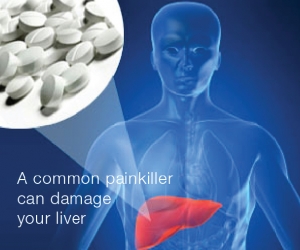
Acetaminophen (Tylenol® or Paracetamol) is the most commonly used painkiller and fever reducing medicine and is easily available over-the-counter. Many people use this drug as if it were candy, without being aware of its likelihood for causing serious, sometimes deadly, consequences when taken in excess. Moreover, acetaminophen is present in small doses in nearly 600 other over-the-counter products in small doses, such as cough and cold drugs, sleep medicines, and in prescription painkillers. Easy access and an abundant presence makes acetaminophen the most common culprit for accidental and potentially life-threatening overdose. Although Acetaminophen is safer than ibuprofen (Motrin®) and aspirin, it has a very narrow safety margin and even a small dosage error can cause serious damage to the liver. Accidental acetaminophen poisoning is the cause of 78,000 emergency room visits per year and is the most common cause of liver failure requiring liver transplants in the United States.