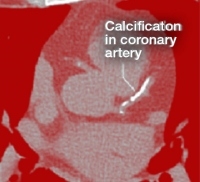
Vitamin C Inhibits Calcification In The Artery Walls
The pharmaceutical industry has successfully made us believe that cholesterol is an undesirable and harmful substance in the body and the lower the cholesterol, the better it is for our health. Statins, the cholesterol-lowering drugs, are the most prescribed drugs worldwide. In addition to decreasing cholesterol, there are also claims of statins having various cardiovascular health benefits. At least 200 million people worldwide are prescribed statins such as lovastatin, atorvastatin, simvastatin and others that are sold under different brand names. However, despite the ever-increasing prescriptions for statins, cardiovascular disease is escalating and continues to be the leading cause of death.
Statins are known to cause serious side effects that are quite often omitted in their promotion. These include irreversible muscle damage, kidney problems, the development of type 2 diabetes, dementia, heart failure, and cancer. One of the important side effects is that statins increase the calcium deposits in the blood vessel walls - the indicator of advanced atherosclerosis and risk of heart attacks.
During the process of atherosclerosis, the body mobilizes different mechanisms to increase the strength and integrity of the arterial walls that is weakened by multi-nutrient deficiency including a deficiency of vitamin C. These processes include wall thickening and formation of atherosclerotic plaque to repair the damaged areas of the arterial walls. An atherosclerotic plaque is made up of cholesterol, calcium, lipid molecules, and cells. Deposition of calcium in the coronary arteries is an important clinical marker for atherosclerosis. It requires transformation of blood vessel cells into osteogenic cells, which are the precursors of bone-forming cells.
In a recent study published by the Dr. Rath Research Institute, the researchers have shown that vitamin C used alone can reduce the calcium accumulation by the cells and block osteogenic transformation of the cells by 20 percent.* The study also confirmed that calcium deposition increases in the presence of statins. However, for the first time we showed that when statins were used together with vitamin C, the calcium deposition reduced by 19 percent. Our results also showed that supplementation of vitamin C was effective in reducing alkaline phosphatase (ALP) by 80 percent. ALP is an important metabolic marker of the calcification process. ALP is an enzyme produced by liver and bone cells and its higher levels are associated with increased calcification leading to an increased risk of fatal heart attacks. These unique findings were awarded a US patent.
While the cholesterol-lowering statins can only mechanically stop the cholesterol production, they are ineffective in reducing the cardiovascular events and deaths. Yet, close to 71 million American adults and 35 percent of young children are prescribed statins. Our study shows that vitamin C is a key micronutrient in the inhibition of coronary calcification, and it has a potential to attenuate the pro-calcification effects of statin drugs.
* V. Ivanov et al., Am J Cardiovasc Dis 2020;10(2):108-116