Healthy skin is the first barrier to prevent any wounds and it is the crucial component in would repair. The skin is the largest organ in the body and it is a mirror of the health of the body’s internal organs. In addition to protection of inner tissue structures, the skin helps in regulation of body temperature and elimination of metabolic waste products.
It is estimated that 6.5 million people in the US struggle with slow wound healing because of various reasons which include diabetes, obesity, and long-term disability such as stroke, spinal cord injury, and multiple sclerosis.
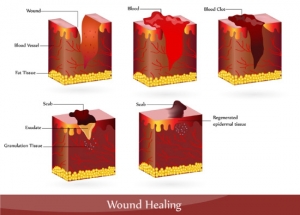
Everybody has experienced wounds either after an injury or surgery and most of the wounds heal naturally in an otherwise healthy person. A wound that does not heal or does not show signs of healing after two weeks is considered a slow-healing or a chronic wound and requires special care from a wound care facility to prevent infection and further complications and to accelerate the recovery process.
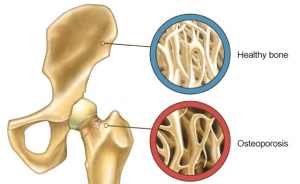
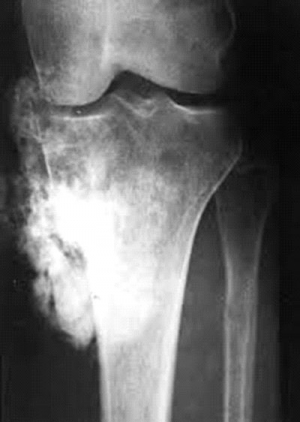
Bone fractures are one of the most painful injuries and require a lengthy recovery time. Everyone is at an equal risk of breaking a bone either from a fall, sports activities, or a car accident. However, bone fractures are more common and take longer to heal in people suffering from osteoporosis.
The most common bone fracture, especially in active adults and children, is a broken leg and often involves a tibial (or shinbone) fracture. In the US, approximately 492,000 tibial fractures are reported every year resulting in close to 400,000 hospital days. The usual time for healing a tibial fracture could be as long as 12 to 16 weeks. This is due to a high incidence of complications requiring strong painkillers for the patient.
It is a popular perception that calcium and vitamin D are essential nutrients for healthy bones. However, few people are aware that bone health largely depends on its protein foundation – the collagen fibers. The alignment of collagen fibers within the bone (its “internal skeleton”) determine how calcium and other minerals are deposited, and therefore healthy collagen is the basis of the strength and stability of the entire bone.
Sarcomas are cancers of connective tissue such as hard tissue (bones), soft tissue (muscles) and tendons. Although sarcomas are uncommon at any age, they are relatively frequent in children. Every year in the USA approximately 1500-1700 children and young people under the age of 20 are diagnosed with bone and soft tissue sarcomas. Sarcomas are one of the most life-threatening cancers in children, and survival ranges from 59%-68% depending on factors such as age, other risks (i.e., tumor location, gender, environment, genetics), prescription medications and other drugs, etc.
The term “connective tissue” is frequently discussed in association with skin or joint disorders, and many people are not aware of how important it is in other chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
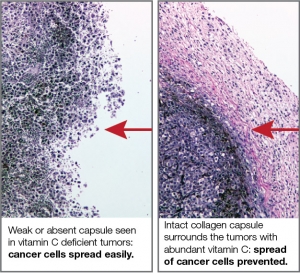
Over 90% of cancer deaths are due to the extensive spread of cancer (metastasis). Cancer cells metastasize by breaking the connective tissue barrier that surrounds them. The strength and stability of connective tissue depends on an optimum production of collagen fibers and the prevention of uncontrolled tissue destruction. An abundant availability of several micronutrients, especially vitamin C, and the amino acids lysine and proline, is essential for this function. Unlike most animals, humans are not capable of internal production of vitamin C and lysine. Yet, most of the cancer research is conducted on mouse models that do produce vitamin C. To overcome this barrier, our research institute utilized a special type of mice that mimic human metabolism in respect to the lack of internal vitamin C production.
Connective tissue is the most abundant type of tissue in our body. The shape and form of the body, including its organs, muscles, bones, and cartilage, are determined by the properties of connective tissue. Skin, blood, blood vessels, adipose tissue (fat cells), tendons, ligaments, and teeth are various examples of connective tissue. Therefore, the term “connective tissue diseases” encompasses a wide range of ailments; some of them are inherited, while others develop as autoimmune diseases due to excessive inflammation. Examples of autoimmune connective tissue diseases are scleroderma, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), mixed connective tissue diseases, etc.