Around the world, more than 200 million people suffer from diabetes, and approximately 18.2 million Americans are affected by this disease. Diabetes is characterized by a high sugar (glucose) level in the blood, which comes as a result of insufficient insulin production in the body, impaired cellular response to it, or both.
Cellular Medicine™ provides a breakthrough in understanding the cause, prevention, and adjunct management of diabetes.
The primary reason why adult onset diabetes (Type II) develops is a long-term deficiency of specific cellular micronutrients that work in synergy in millions of cells in the pancreas (the organ that produces insulin), the liver, and the blood vessels walls. This new understanding also explains the reason for most severe consequences of diabetes, which are circulatory problems. Diabetes significantly increases the chance of developing atherosclerotic deposits, which by clogging the blood vessels can increase the risk of heart attacks, feet amputation or blindness etc.
This concept was tested in a pilot clinical trial in patients with Type II diabetes.
Aim of the Study
To test the effectiveness of the specific combination of cellular nutrients on blood sugar levels in patients suffering from Type II diabetes.
Study Design
Pilot clinical study was conducted in 10 patients suffering from Type II Diabetes also called adult onset diabetes. These patients took a specific micronutrient program comprising vitamins, amino acids and minerals, such as chromium, for 6-months. Blood tests were conducted to measure the effect of this nutrient synergy on blood glucose levels as well as HbA1-c levels (indicator of damage to red blood cells by glucose). before using this micronutrient program, after two months, after four months and after six months of its use.
Study Results
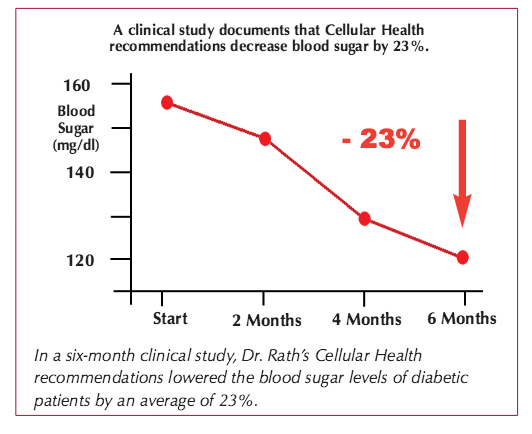 After 6 months of following the Cellular micronutrients program there was a decrease in blood sugar level by 23 % (from an average of 155mg/dl at the beginning of the study to 120 mg/dl at the end of the study). In addition, the HbA1-c levels in the blood were lower by an average of 9.3%.
After 6 months of following the Cellular micronutrients program there was a decrease in blood sugar level by 23 % (from an average of 155mg/dl at the beginning of the study to 120 mg/dl at the end of the study). In addition, the HbA1-c levels in the blood were lower by an average of 9.3%.
Conclusion
This six-month pilot study, though conducted with a small group of patients, confirmed the positive effects of the synergistic combination of cellular nutrients on regulating blood sugar levels in diabetic patients without any side effects. The effectiveness of the synergistic action of nutrients in type II diabetes has been further confirmed by several testimonials based on patient medical records.